Introduction to the Labor Market
Understanding the labor market is critical for policymakers, business leaders, and job seekers alike. Labor market insights provide key information about employment trends, wage rates, supply and demand of labor, and overall market health. These insights help businesses make informed decisions on hiring strategies, compensation, and talent development, while individuals can use this knowledge to make career choices. In this comprehensive pillar page, we’ll explore every aspect of the labor market to give you a detailed understanding of its mechanics, trends, and implications for various stakeholders.
What is the Labor Market?
So, what is the labor market? Broadly, the labor market refers to the interaction between employers and workers, where businesses demand labor and individuals supply it. It is the mechanism through which wages are set, employment is determined, and the distribution of talent is facilitated. The labor market meaning can be understood as a network of economic exchanges in which employees offer their labor services in return for wages. Essentially, it’s the marketplace where work is bought and sold.
Understanding Labor Market Definition
The labor market definition includes the supply of workers available and the jobs provided by employers. It’s a dynamic system influenced by various factors such as economic growth, globalization, education, and technology. A well-functioning labor market aligns the skills of workers with the needs of employers, ensuring optimal productivity and innovation.
Understanding How the Labor Market Operates
The labor market functions based on the principles of supply and demand. Employers demand labor to produce goods and services, while individuals supply labor to earn wages. In a perfectly competitive labor market, wages are determined by the intersection of supply and demand. However, in the real world, various factors such as government regulations, union activities, and market imperfections can affect labor market outcomes.
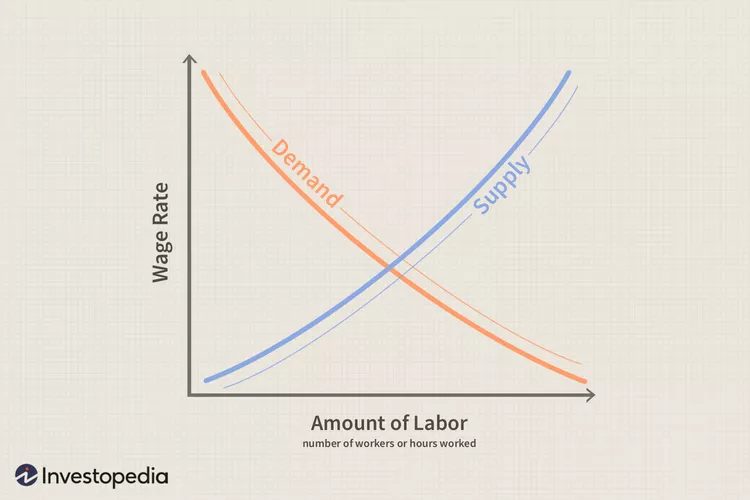
Image Source: Investopedia
Key components that influence the labor market include:
- Economic conditions: Economic growth stimulates job creation as businesses expand and demand for goods and services rises, increasing the need for labor. Conversely, economic downturns like recessions result in company cutbacks, hiring freezes, and layoffs, leading to decreased job availability and heightened competition among job seekers.
- Education and skills: A workforce equipped with relevant skills and qualifications is crucial for maintaining high productivity and enhancing competitiveness. When the talent pool has in-demand skills, businesses thrive, and job opportunities increase, while gaps in skills can lead to labor shortages in specialized fields.
- Technology: Automation and advancements in technology are reshaping the labor market. While some roles become obsolete due to automation, digital transformation often leads to the creation of new jobs in tech and other emerging sectors, highlighting the need for adaptability and upskilling.
- Globalization: A connected global labor market allows employers to source talent from around the world, impacting job availability and wage standards locally. This access can lead to greater diversity and specialization in certain sectors but may also intensify wage competition across regions.
Key Concepts in the Labor Market You Should Know
Understanding key labor market concepts is essential for navigating or analyzing workforce trends. These foundational terms provide insight into labor dynamics, workforce availability, and economic health.
- Labor Force Participation Rate
This metric reflects the percentage of working-age individuals (typically aged 15-64) who are either employed or actively seeking employment. A high participation rate generally indicates a robust workforce and greater economic engagement, while a lower rate may highlight challenges such as discouraged workers or demographic shifts. - Unemployment Rate
A primary measure of labor market health, the unemployment rate represents the percentage of individuals who are actively seeking work but have not secured employment. High unemployment rates may signal economic downturns, whereas low rates often indicate a strong job market. It’s a critical gauge for economists to assess job availability and economic stability. - Wage Rate
This is the average compensation workers receive for their labor, often measured hourly or annually. Wage rates vary by industry, region, and occupation and are influenced by factors such as education levels, skill demand, and economic conditions. Wage trends help track shifts in purchasing power and income distribution. - Job Vacancies
The number of unfilled positions available in the labor market indicates labor demand. High vacancy rates suggest a strong demand for workers, which can drive wages up, especially in sectors facing skill shortages. Monitoring job vacancies helps employers and policymakers understand where talent gaps exist and address workforce needs.
How the Labor Market Shapes Employment and Wages?
In the labor market, a variety of activities occur that determine employment rates, wage levels, and the distribution of labor. Employers post job vacancies, job seekers apply for positions, and wages are negotiated. The market is also shaped by policy decisions, economic shifts, and demographic changes.
One key area of interest in labor market analysis is the employment outcomes for college graduates, which vary significantly by major. Graduates in fields like technology, healthcare, and engineering often have higher employment rates and better wage prospects than those in the arts or humanities. Understanding labor market data related to college majors can help students make informed decisions about their education paths.
Labor Market Trends & Analysis
Labor market trends give us insights into current conditions and future projections. Businesses, policymakers, and individuals can benefit from analyzing labor market data to identify opportunities and challenges.
Current Labor Market Trends
The current labor market has been shaped by factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic, technological advancements, and globalization. As of 2024, labor market trends indicate a growing demand for workers in technology, healthcare, and renewable energy sectors. Remote work and gig economy jobs continue to be significant trends, while automation is transforming industries like manufacturing and logistics.
Analyzing Labor Market Data and Statistics
Labor market analysis involves reviewing data on employment rates, wage growth, and job vacancies to understand overall economic health. Common labor market indicators include the unemployment rate, labor force participation rate, and job openings. Analyzing labor market data helps businesses and policymakers make informed decisions about hiring, wage setting, and training programs.
Insights and Reports on the Labor Market
Numerous labor market insights can be drawn from reports published by government agencies, academic institutions, and private organizations. For example, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) provides detailed data on employment trends, industry growth, and wage statistics, offering a clear picture of the current labor market conditions.
Labor Market Impact Assessment
Assessing the impact of various factors on the labor market is crucial for understanding how changes in policy, technology, or the economy affect employment. Labor market impact assessments evaluate how events like minimum wage increases or the rise of automation influence job availability and wage levels.
Labor Market Projections for 2025
Looking ahead, labor market projections for 2024 suggest continued growth in technology-related sectors, healthcare, and sustainable energy. However, the market will also face challenges from automation, demographic shifts, and geopolitical instability. Companies and workers alike must adapt to these changes to remain competitive.
How Different Labor Market Types & Theories Shaping Employment?
Labor market theories help us understand the different ways in which labor markets can function. The key types of labor markets include:
1. Perfectly Competitive Labor Market
In a perfectly competitive labor market, numerous employers compete for workers, and wages are set by supply and demand. This type of market assumes that no single employer or worker has the power to influence wage rates.
2. Monopsony and Monopsonistic Labor Markets
In a monopsony labor market, a single employer dominates the market, giving them significant control over wage rates and employment terms. This often leads to lower wages and fewer job opportunities.
3. Understanding the Dual and Split Labor Markets
A dual labor market refers to the existence of two separate segments: the primary market, which offers high wages and job security, and the secondary market, which offers low wages and precarious working conditions. Understanding this concept is crucial for analyzing labor market inequality.
4. Primary vs. Secondary Labor Markets
Primary labor markets are characterized by well-paying jobs, opportunities for advancement, and job security. In contrast, secondary labor markets offer lower wages, limited benefits, and less job stability.
5. Labor Market Segmentation and Dynamics
Labor market segmentation occurs when workers are divided into different groups based on factors like education, skills, or demographics. This segmentation leads to different labor market outcomes for different groups, affecting wage levels and employment rates.
Understanding the Factors & Measures Influencing the Labor Market
Various factors influence labor market outcomes, including economic conditions, government policies, and technological developments.
What 5 Key Factors Influence the Labor Market Today?
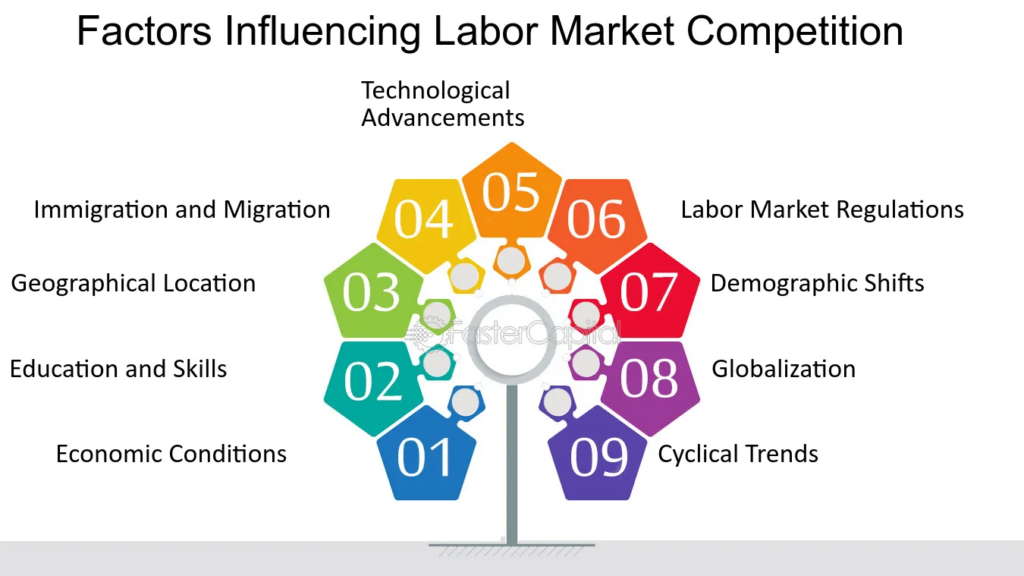
Image Source: FasterCapital
- Economic Growth:
Economic growth is a primary driver of job creation and wage increases. When an economy is expanding, businesses tend to grow, leading to higher demand for workers. This growth not only creates more job opportunities but can also lead to increased wages as companies compete to attract talent. Conversely, during economic downturns, job availability often declines, and wage growth slows. - Education and Skills:
In today’s job market, having higher education and specialized skills provides a significant advantage. Job seekers with advanced qualifications or expertise in high-demand areas tend to secure better job prospects, often with higher starting salaries and greater long-term earning potential. As industries evolve, continuous learning and upskilling have become essential for career growth and stability. - Technological Advancements:
Technological progress, especially in automation and artificial intelligence, is transforming the labor market. While new technologies create demand for tech-savvy workers, they can also render some roles obsolete, particularly in routine or manual tasks. This dual impact requires workers and businesses to adapt, pushing more people towards careers in technology, data analysis, and other emerging fields. - Government Policies:
Labor market conditions are heavily influenced by government policies, including minimum wage laws, labor protections, and employment standards. Policies on tax incentives, worker rights, and job creation programs can all affect wage levels, job availability, and overall employment quality. For instance, minimum wage increases directly impact low-wage sectors, influencing both wages and employment rates. - Globalization:
The interconnected global economy affects local labor markets, particularly through outsourcing and international trade. For developed countries, globalization can lead to job outsourcing, influencing wage rates in certain sectors. Meanwhile, developing nations may experience job growth in sectors such as manufacturing and customer service. However, this trend also introduces wage competition, impacting labor costs worldwide.
How to Measure Wage Inflation in the Labor Market?
Wage inflation refers to the increase in wages over time, often driven by factors such as economic growth, labor shortages, and cost of living increases. It’s a key indicator of labor market health.
Wage rates in the labor market fluctuate based on supply and demand. In high-demand industries, wages tend to rise, while industries facing an oversupply of labor may see stagnant or declining wages.
Wage rates are influenced by a variety of factors, including worker productivity, industry demand, education levels, and regional economic conditions. Understanding these factors is crucial for analyzing labor market trends.
How Labor Market Research Drives Employment Strategies?
Conducting thorough labor market research is essential for understanding market dynamics, trends, and opportunities.
Conducting Labor Market Research
Labor market research involves gathering data on employment trends, wage levels, and industry growth. This research helps businesses and policymakers make informed decisions about hiring, training, and wage policies.
Labor Market Research Tools and Software
Several labor market research tools and software platforms are available to help businesses and individuals analyze market data. Popular tools include government databases like the U.S. BLS, as well as private platforms like LinkedIn’s Economic Graph.
Labor Market Analysis Tools
Labor market analysis tools help employers and job seekers understand current market conditions, forecast trends, and identify opportunities for growth. Tools like Burning Glass Technologies and EMSI provide detailed labor market data and projections.
Interpreting and Applying Labor Market Data
Interpreting labor market data involves analyzing trends and statistics to draw meaningful insights. These insights can be used to inform hiring strategies, wage negotiations, and workforce development programs.
Legislation & Policy in the Labor Market
Government policies play a significant role in shaping labor market outcomes. Legislation can affect wage levels, employment rates, and worker protections.
Impact of Minimum Wage on the Labor Market
Minimum wage laws set a floor for wages, preventing employers from paying workers below a certain level. While minimum wage increases can boost incomes for low-wage workers, they may also lead to reduced hiring or increased automation in some industries.
Labor Market Conditions and Key Indicators
Key labor market indicators, such as unemployment rates and job vacancy rates, provide insights into the overall health of the labor market. Policymakers use these indicators to assess economic conditions and guide policy decisions.
Exploring the Role of Government Policies in Labor Markets
Government policies, including labor protections, wage regulations, and workforce development initiatives, influence labor market outcomes. For example, policies promoting education and training can help reduce skill gaps and improve employment rates.
How Legislation Affects Labor Market Outcomes?
Legislation such as labor laws, wage regulations, and worker protections significantly impacts labor market outcomes. For example, strong labor laws can improve job security and working conditions, while weak regulations may lead to exploitation and wage stagnation.
Regional & Global Labor Markets

Image Source: Market Research Intellect
Labor markets vary significantly across regions and countries, with different economic conditions, policies, and workforce characteristics shaping each market.
Current Global Labor Market Trends and Predictions
The global labor market is influenced by factors such as economic globalization, technological advancements, and demographic changes. Current trends include a growing demand for skilled labor in tech and healthcare sectors and the rise of remote work.
Labor Market Differences Across Regions
Labor market conditions vary across regions due to factors such as economic development, education levels, and government policies. For example, developed countries often have more robust labor markets with higher wages and job security, while developing countries may experience higher levels of informal employment and wage disparities.
Country-Specific Labor Markets
Labor markets in developed countries tend to offer higher wages, better working conditions, and more job security compared to those in developing countries. However, developing countries often have faster-growing labor markets due to population growth and economic development.
1. US Labor Market:
The US labor market is characterized by low unemployment rates, high demand for skilled labor, and wage growth in certain sectors. However, challenges such as wage inequality and automation remain.
2. China Labor Market:
China’s labor market is undergoing significant changes due to automation, an aging population, and economic restructuring. The demand for skilled workers in technology and manufacturing sectors is increasing.
3. Canada Labor Market:
The labor market in Canada is strong, with low unemployment and high demand for workers in healthcare, technology, and skilled trades. Immigration plays a key role in meeting labor shortages.
4. UK Labor Market:
The UK labor market faces challenges such as Brexit-related disruptions and automation but also offers opportunities in growing sectors like technology, healthcare, and finance.
Comparing Labor Markets in Developed and Developing Countries
Overcoming Labor Market Challenges & Opportunities for Future Growth
The labor market faces several challenges, including unemployment, skill gaps, and the impact of technology. However, these challenges also present opportunities for growth and innovation.
Addressing Unemployment and Skill Gaps
Unemployment and skill gaps are significant challenges in many labor markets. Addressing these issues requires investment in education, training, and workforce development programs.
Market Disruptions from Technology and Automation
Technology and automation are reshaping the labor market by eliminating certain jobs and creating new ones. Workers need to adapt by acquiring new skills and embracing lifelong learning.
The Role of Education and Training
Education and training are critical to labor market success. Workers with higher levels of education and specialized skills tend to have better job prospects and higher wages.
Strategies for Navigating Labor Market Volatility
To navigate labor market volatility, workers and businesses must remain adaptable. This includes investing in education and training, embracing technology, and staying informed about labor market trends.
Conclusion
The labor market is a complex and dynamic system influenced by various factors, including economic conditions, government policies, and technological advancements. Understanding labor market insights is crucial for making informed decisions in today’s rapidly changing economy.
Looking ahead, the labor market will continue to evolve as technology, globalization, and demographic shifts shape employment trends. By staying informed and adapting to these changes, businesses and workers can thrive in the labor market of the future.From supply-demand trends to wage rates and industry shifts, JobsPikr provides the real-time data you need to stay ahead in workforce strategy and planning. Don’t miss the chance to elevate your decision-making—sign up now and gain access to actionable labor market data today!



